Advancements in Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engines: Overcoming Challenges for a Sustainable Future
Key Ideas
- Hydrogen emerges as a promising energy source for internal combustion engines (ICEs) with unique properties leading to near-zero pollutant emissions and high efficiency.
- Research focuses on overcoming challenges such as wider combustible limits, lower ignition energy, preignition, and knock through strategies like stratified combustion, injection timing, and exhaust gas regulation.
- Nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions remain a challenge for hydrogen ICEs, with research suggesting using lean combustion, rich combustion, and three-way catalysts to minimize emissions effectively.
- Studies on variable valve timing, injection strategies, and EGR technology show potential in improving combustion efficiency and reducing NOx emissions in hydrogen internal combustion engines.
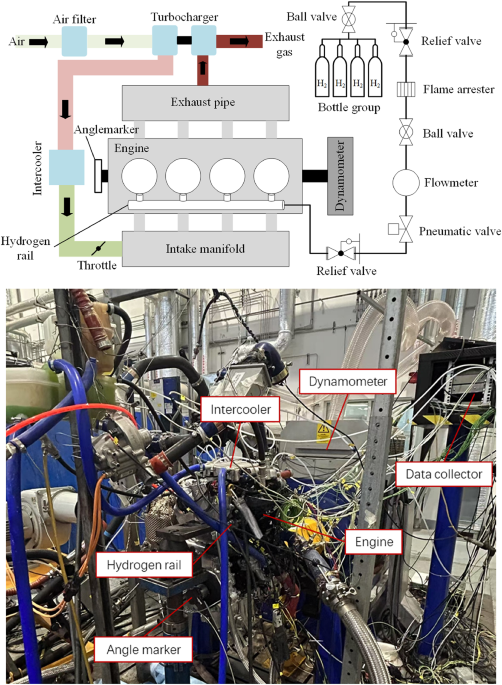
As the world faces depleting fossil fuel reserves and escalating environmental concerns, the quest for sustainable energy solutions gains momentum. The article delves into the transformative potential of hydrogen as an alternative fuel for internal combustion engines (ICEs), emphasizing its advantages in reducing carbon emissions and enhancing efficiency. Hydrogen's fast combustion rate, wide combustible limit, and minimal pollutant emissions position it as a viable candidate for powering ICEs, with remarkable thermal efficiencies exceeding 35% and even reaching over 70% in innovative designs.
Despite the promising aspects of hydrogen as a fuel, challenges persist in optimizing its combustion within ICEs. Researchers are actively exploring strategies like stratified combustion, precise injection timing, and exhaust gas regulation to address issues such as preignition, knock, and wider combustible limits. These endeavors aim to unlock the full potential of hydrogen-powered engines by enhancing efficiency and power density.
A critical concern highlighted in the article is the generation of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in hydrogen ICEs due to high-temperature combustion processes. The discussion underscores the significance of maintaining optimal air-fuel ratios, utilizing lean and rich combustion strategies, and leveraging three-way catalysts to mitigate NOx emissions effectively. Moreover, studies on variable valve timing, injection optimization, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) demonstrate promising avenues for improving combustion efficiency while curbing NOx emissions.
In essence, the article paints a positive outlook on the role of hydrogen internal combustion engines in fostering a sustainable energy landscape. Despite existing challenges, ongoing research and technological innovations offer valuable insights and solutions to propel the adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source for ICEs, paving the way for a greener and more efficient future.
Topics
Production
Environmental Impact
Energy Efficiency
Alternative Fuels
Emission Reduction
Thermal Efficiency
Combustion Strategies
Latest News