Revolutionizing PEMFC Durability with Water-Soluble Fullerene Derivatives
Key Ideas
- Novel fullerene derivatives show promise in inhibiting radical-induced degradation of PEMs in fuel cells.
- Water-soluble and stable fullerene derivatives act as radical scavengers and Ce anchors within Nafion matrices.
- Enhanced proton conductivity and mechanical stability achieved through innovative chemical modifications.
- Insights gained from this study contribute to advancing PEMFC durability and performance.
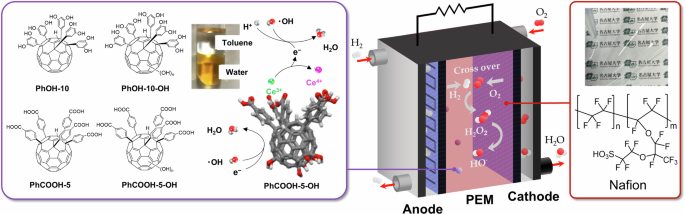
This study focuses on addressing the durability challenges faced by proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) through the development of innovative fullerene derivatives. The research highlights the detrimental effects of radical-induced degradation on PEMs in fuel cells and introduces a solution using water-soluble fullerene derivatives as radical scavengers and Ce anchors within Nafion matrices. By enhancing proton conductivity and mechanical stability, these novel derivatives aim to inhibit membrane thinning and pinhole formation, thereby improving PEMFC longevity. The study details the synthesis and properties of these derivatives, showcasing their high solubility in polar solvents and water, essential for compatibility with Nafion membranes. Furthermore, the introduction of phenolic and benzoic acid groups at specific positions on the fullerene structure enhances radical scavenging ability and water dispersibility. The innovative approach of combining fullerene derivatives with Ce ions demonstrates promising results in mitigating oxidative degradation and enhancing dispersion within the membrane. Overall, this groundbreaking research provides valuable insights into radical-scavenging materials and their pivotal role in advancing the durability and performance of PEMFCs.
Topics
Fuel Cells
Power
Antioxidants
Proton Conductivity
Nafion Membranes
Radical Scavengers
Fullerene Composites
Latest News