Revolutionizing Ammonia Production: Solar-Powered Catalytic Reaction Offers Sustainable Alternative
Key Ideas
- Traditional ammonia production has a high energy cost and significant carbon dioxide emissions, driving researchers in Japan to develop a solar-powered catalytic system for a cleaner alternative.
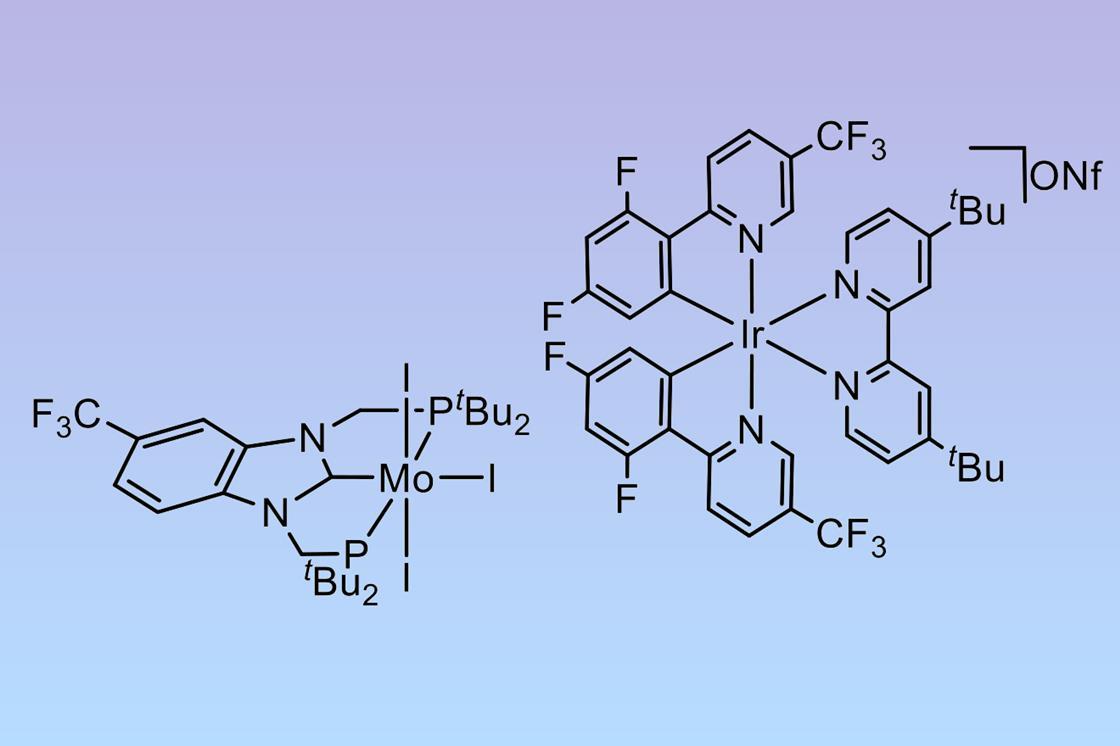
- The new system, utilizing molybdenum and iridium catalysts along with a tertiary phosphine reagent, showed a quantum efficiency of over 22%, surpassing other photocatalytic methods in efficiency.
- Experts, like computational chemist William Goddard, praise the development as a significant advancement, envisioning global applications for sustainable ammonia production in agriculture.
- Future plans for the research team include optimizing the system for integration into green ammonia supply chains by reducing costs, enhancing catalyst durability, and minimizing the required tertiary phosphine.
A groundbreaking development in ammonia production has emerged from Japan, where researchers have devised a new catalytic system that transforms atmospheric nitrogen and water into ammonia with sunlight as the sole energy source. Traditional ammonia production, predominantly through the energy-intensive Haber–Bosch process, has incurred substantial carbon dioxide emissions. This innovation aims to mitigate the environmental impact by providing a more sustainable and efficient method. The team, led by Yoshiaki Nishibayashi, has successfully adapted the system to utilize water as a hydrogen source, overcoming the challenge posed by water's stability.
The innovative system involves molybdenum and iridium catalysts alongside a tertiary phosphine reagent that activates the water molecules. Through a series of catalytic reactions, including the activation of dinitrogen and conversion to ammonia, the process achieves a remarkable quantum efficiency exceeding 22%. This efficiency milestone has drawn praise from experts like William Goddard, who envisions widespread implementation of this technology to revolutionize ammonia production for fertilizers globally.
Looking ahead, the research team is committed to refining the system for seamless integration into green ammonia supply chains. This involves streamlining processes to reduce tertiary phosphine usage, optimizing catalyst costs, and enhancing their longevity. The collaborative efforts of these researchers signify a significant step towards establishing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to ammonia production, with far-reaching implications for the agricultural industry and beyond.