The Evolution of Water Electrolysis: From 19th Century Discovery to Modern Green Hydrogen Production
Key Ideas
- Water electrolysis, discovered in the 19th century, is now a promising method for storing excess renewable energy as green hydrogen.
- Hydrogen produced through electrolysis can be used in various applications like combustion processes, methanation, fuel cell regeneration, and ammonia production.
- Fuel cell drives with hydrogen are a promising alternative for long-distance vehicles with high energy densities, offering environmental advantages over batteries.
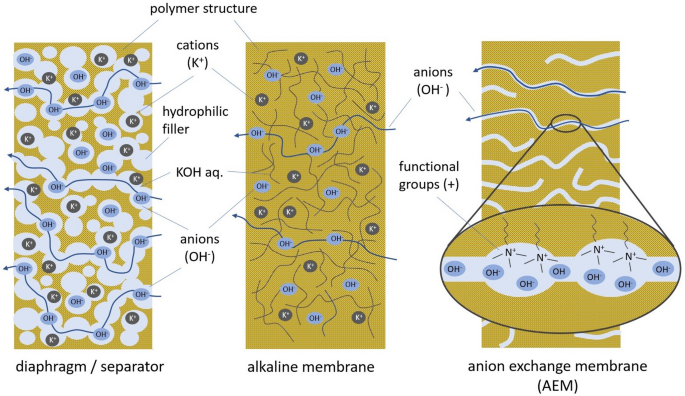
- Modern advancements in water electrolysis include solid polymer electrolytes and anion exchange membranes, improving efficiency and reducing the use of precious metals.
Water electrolysis, a process discovered in the 19th century, has evolved into a promising method for storing excess renewable energy as green hydrogen. The hydrogen produced through electrolysis finds applications in combustion processes, methanation, fuel cell regeneration, and ammonia production. In the energy sector, fuel cell drives utilizing hydrogen are emerging as a sustainable alternative for long-distance vehicles due to their high energy densities and lower environmental impact compared to batteries. The article discusses the challenges associated with high-pressure requirements for hydrogen in various industrial processes like ammonia production and steel manufacturing. It emphasizes the importance of green hydrogen production for a sustainable future energy system. Modern advancements in water electrolysis, such as solid polymer electrolytes and anion exchange membranes, are highlighted for their superior efficiency and reduced reliance on precious metals like platinum and iridium. The article also touches on the economic advantages of electrolysis and the development of alkaline electrolyzers using non-precious metals as catalysts. Overall, the sentiment of the article towards hydrogen is positive, showcasing its potential in revolutionizing energy storage and sustainable industrial processes.
Topics
Fuel Cells
Green Hydrogen
Renewable Energy
Sustainability
Electric Vehicles
Energy Efficiency
Energy Storage
Materials Science
Chemical Industry
Latest News