Breakthrough in Green Hydrogen Production: South Korean Researchers Develop High-Efficiency Solar System
Key Ideas
- South Korean researchers at UNIST have developed a high-efficiency artificial leaf system that directly produces hydrogen from sunlight and water, without external electricity or carbon emissions.
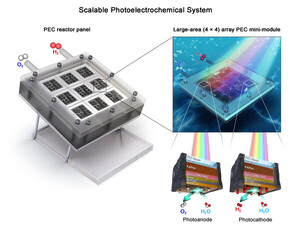
- The system achieved a record 11.2% solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency at the module level, surpassing previous limitations of low efficiency, durability, and scalability.
- The breakthrough was made possible by utilizing a perovskite-based photoelectrode with nickel-iron-cobalt catalysts, ensuring long-term stability and scalability into large-area panels for real-world deployment.
- Funded by Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT and the Institute for Basic Science, this research paves the way for green hydrogen to become a significant player in the global hydrogen economy, offering a clean fuel alternative to fossil energy.
In a significant development towards carbon-neutral energy, researchers at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology in South Korea have created a groundbreaking solar system that directly generates hydrogen from sunlight and water, without the need for external electricity or carbon emissions. The innovative artificial leaf technology, inspired by natural photosynthesis, aims to produce green hydrogen as a clean fuel alternative to traditional fossil energy sources. By eliminating the electrical conversion step in conventional systems, this modular artificial leaf reduces system losses, spatial footprint, and environmental impact. The team at UNIST overcame challenges of low efficiency and limited durability by incorporating a perovskite-based photoelectrode with nickel-iron-cobalt catalysts, achieving a remarkable 11.2% solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency at the module level – the highest reported to date. The system's chlorine-doped perovskite absorber ensures efficient light capture, while UV-resistant transport layers and advanced catalyst protection contribute to long-term stability. The research, published in Nature Communications, demonstrates that commercial applications of this technology are now feasible, with modules retaining 99% of their performance after continuous operation under sunlight and moisture. Supported by funding from Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT and the Institute for Basic Science, this breakthrough holds immense promise for the global hydrogen economy, offering a sustainable energy solution amid increasing concerns about carbon-intensive practices in energy production.
Topics
Production
Renewable Energy
Technology
Innovation
Sustainability
Research
Solar Energy
Perovskite
Scientific Advancement
Latest News